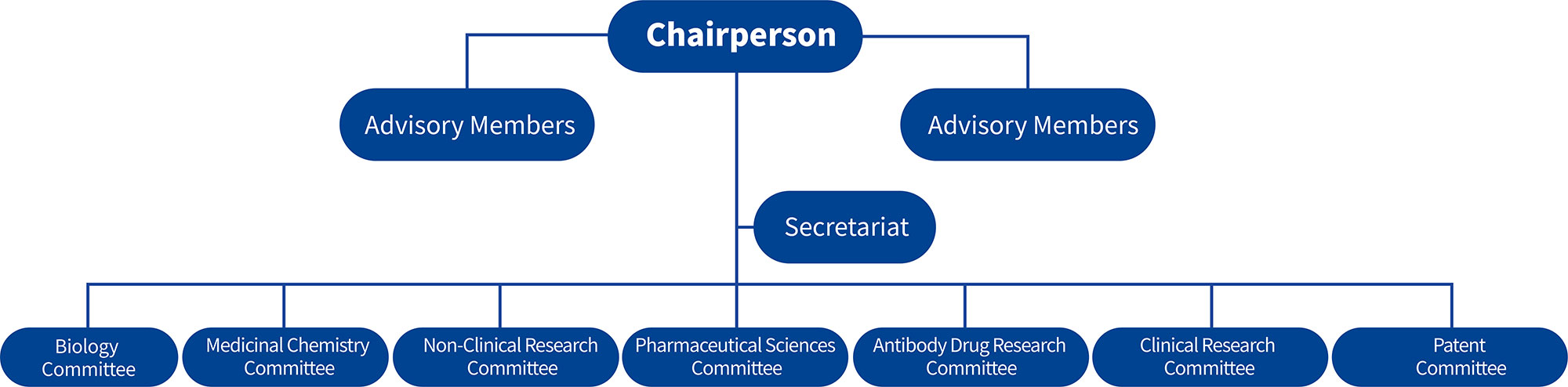
The Scientific Committee serves as the core strategic advisory and decision-making support body of Chipscreen Biosciences, bringing together senior scientists and industry experts across the entire R&D chain, including drug discovery, preclinical research, clinical development, production processes, regulatory submissions, market access, and intellectual property. Through institutionalized and systematic approaches, the Committee synergistically promotes the deep integration of scientific innovation and R&D efficiency, on one hand stimulating researchers' capacity for free exploration in cutting-edge fields, while consistently adhering to clinical value orientation, strengthening academic rigor and translational feasibility. Relying on multidimensional scientific evidence and cross-departmental collaborative validation, the Committee ensures the efficient allocation of R&D resources toward the most valuable and translationally promising directions, continuously empowering the output of highly valuable innovative outcomes.